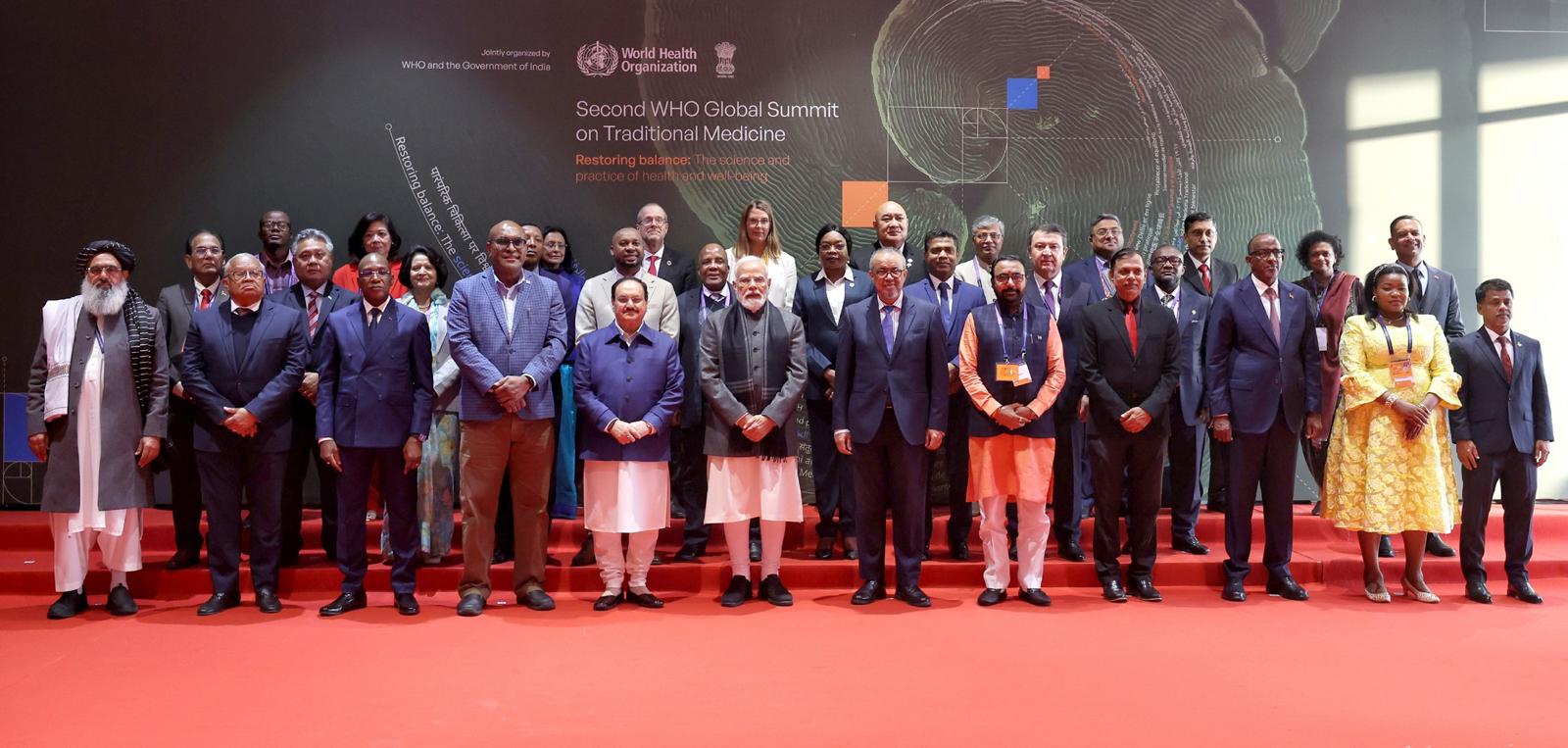
The global health community recently convened in New Delhi for a landmark event, the second World Health Organization (WHO) Global Summit on Traditional Medicine, co-hosted with the Government of India. This significant gathering, marking a pivotal moment in the trajectory of global health policy, brought together an expansive network of stakeholders: over 800 delegates from more than 100 countries, including health ministers from over 20 nations, augmented by more than 16,000 online participants. The summit’s core mission was to articulate and implement a forward-looking strategy for integrating traditional, complementary, and integrative medicine (TCIM) into mainstream healthcare systems, emphasizing the pursuit of safe, evidence-based, and affordable care. This collaborative effort signaled a decisive shift in how diverse healing practices, deeply embedded in centuries of cultural heritage across the globe, are perceived and leveraged within modern public health frameworks.
At the heart of the summit’s achievements was the unanimous endorsement of the Delhi Declaration, a seminal document that enshrines the collective commitment of 26 Member States to elevate traditional medicine from a state of mere recognition to one of active and systematic integration. This declaration represents a profound evolution in global health policy, underscoring a shared understanding that TCIM must become an intrinsic component of primary health care services. The signatory nations pledged to undertake several critical actions: fortifying regulatory and safety standards for traditional practices, substantially increasing investment in rigorous scientific research to validate their efficacy and safety, and establishing interoperable data systems to meticulously track patient outcomes and overall impact. The overarching vision articulated is for traditional medicine to transcend its historical role as a parallel system, instead becoming a vital catalyst for achieving universal health coverage by offering patient-centered, culturally sensitive, and holistic care solutions that complement conventional medical approaches.
The strategic impetus behind this renewed global focus on traditional medicine is multifaceted, driven by an acknowledgment that these ancient healing modalities offer unique advantages in addressing some of the most pressing contemporary health challenges. As Dr. Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, the WHO Director-General, eloquently conveyed, the Delhi Commitment provides a tangible roadmap, elucidating "not only why traditional medicine matters – but on how to act." He highlighted the inherent potential of TCIM to alleviate the escalating burden of noncommunicable diseases, rectify pervasive inequities in access to essential health services, and even bolster community resilience in the face of health impacts exacerbated by climate change. This perspective positions traditional medicine as a valuable, often cost-effective, and culturally resonant resource capable of augmenting and diversifying conventional medical interventions, particularly in underserved regions where access to modern healthcare infrastructure remains limited. Its emphasis on prevention, lifestyle, and holistic well-being aligns well with sustainable healthcare models.
To provide a robust foundation for this ambitious integration, a cornerstone initiative unveiled at the summit was the Traditional Medicine Global Library (TMGL). This groundbreaking digital platform is envisioned as the world’s first comprehensive, centralized repository for traditional medicine knowledge, consolidating an expansive collection exceeding 1.6 million resources. The TMGL’s content spans a vast spectrum, from meticulously peer-reviewed scientific studies and clinical trials to carefully preserved Indigenous knowledge systems and historical texts. Its primary objective is to bridge long-standing gaps in information accessibility and validation, fostering a more transparent and evidence-driven discourse around TCIM. Equipped with advanced analytical features such as Evidence Gap Maps, which visually pinpoint areas requiring further scientific investigation, and an AI-powered tool, TMGL GPT, the library is poised to democratize access to credible information, significantly accelerate scientific inquiry, and empower evidence-based decision-making for policymakers, researchers, and practitioners worldwide. This digital infrastructure is indispensable for moving beyond anecdotal evidence, towards robust, verifiable data that will enhance the credibility, safety, and utility of traditional practices within integrated health systems.
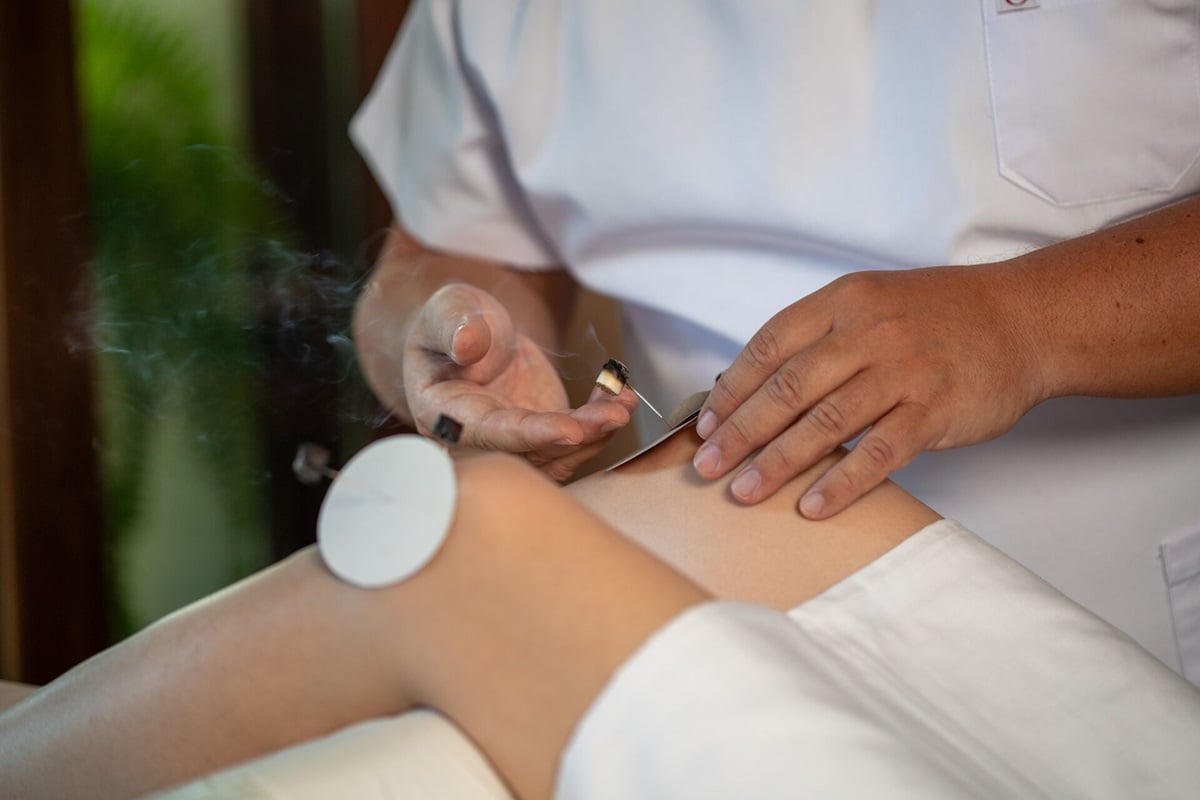
Further underscoring the commitment to innovation, the summit also championed the launch of Health & Heritage Innovations (H2I). This forward-looking initiative is designed to cultivate and nurture breakthrough ideas that ingeniously merge time-honored traditional healing practices with cutting-edge technologies. H2I envisions a future where advancements in artificial intelligence, genomics, and digital health tools serve to enhance, rather than supplant, the profound wisdom embedded in ancient healing traditions. Examples might include AI-driven analysis of complex herbal formulations to identify active compounds, genomic studies to understand individual responses to traditional therapies, or digital platforms for delivering personalized traditional health interventions. From over a thousand compelling proposals submitted globally, 21 finalists were carefully selected, embarking on an intensive year-long acceleration program. This program is meticulously structured to provide crucial support for refining prototypes, offering expert scientific and regulatory guidance to ensure safety and compliance, and facilitating strategic connections with key policymakers and potential investors. The ultimate goal is to transform these promising concepts into scalable, impactful solutions that can be safely, effectively, and ethically integrated into diverse healthcare settings worldwide.
Guiding the intricate implementation of these ambitious strategies is the newly established Strategic and Technical Advisory Group on Traditional, Complementary and Integrative Medicine (STAG-TM). Comprising 19 independent experts drawn from a broad array of disciplines, STAG-TM will function as a critical advisory body to the overarching WHO Global Traditional Medicine Strategy 2025–2034. Its comprehensive mandate includes shaping global research priorities to fill critical evidence gaps, developing international standards for both traditional practices and products to ensure quality and safety, and offering strategic advice on the seamless and ethical integration of TCIM into national health systems. During its inaugural meeting, held in conjunction with the summit, the group swiftly identified several urgent priorities: robust evidence generation through rigorous research, the crucial preservation and respectful documentation of traditional knowledge, leveraging digital innovation for data management and accessibility, and comprehensive capacity building across Member States to train practitioners and integrate services effectively. These focused areas are vital for ensuring that traditional medicine’s integration is systematic, ethical, sustainable, and yields measurable improvements in public health outcomes.
The palpable energy and enthusiasm witnessed in New Delhi, frequently remarked upon by participants, profoundly underscored a collective urgency and shared vision among the diverse assembly of ministers, scientists, Indigenous leaders, and traditional practitioners. The summit transcended being merely a forum for dialogue; it represented a decisive inflection point towards concrete, actionable commitments. The collective resolve embodied in the Delhi Declaration, coupled with the strategic launch of these interconnected initiatives—the TMGL, H2I, and STAG-TM—signifies the dawn of a new chapter for traditional medicine. This era is characterized by a concerted global effort to responsibly and scientifically harness its immense potential, moving away from historical marginalization towards strategic inclusion.
Looking ahead, the World Health Organization, in close collaboration with its Member States, is fully committed to translating these pledges and strategic frameworks into tangible realities on the ground. The comprehensive roadmap involves systematically scaling access to trusted knowledge, continually accelerating innovation in TCIM through research and technological integration, and embedding these culturally significant and often effective practices into health systems globally. The overarching WHO Global Traditional Medicine Strategy 2025–2034, which received substantial advancement through the summit’s outcomes, articulates a bold and transformative trajectory. It envisions a future for healthcare that is inherently more inclusive, deeply rooted in diverse cultural contexts, and robustly resilient in its capacity to address both existing and emerging health challenges. This holistic and comprehensive approach aims to unlock the full, responsible potential of traditional medicine, ensuring it contributes meaningfully to the health, well-being, and equitable access to care for populations worldwide.